Fluorspar (CaF2)

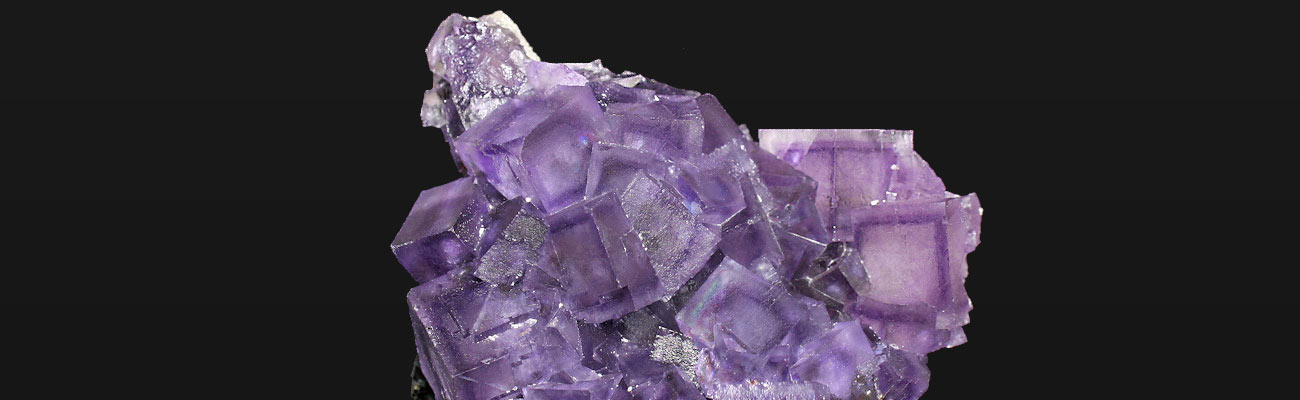
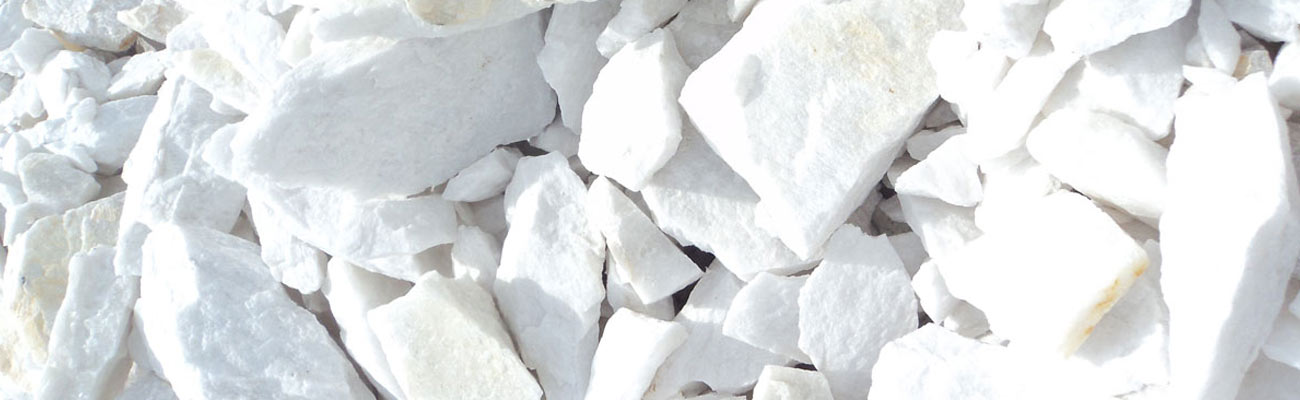
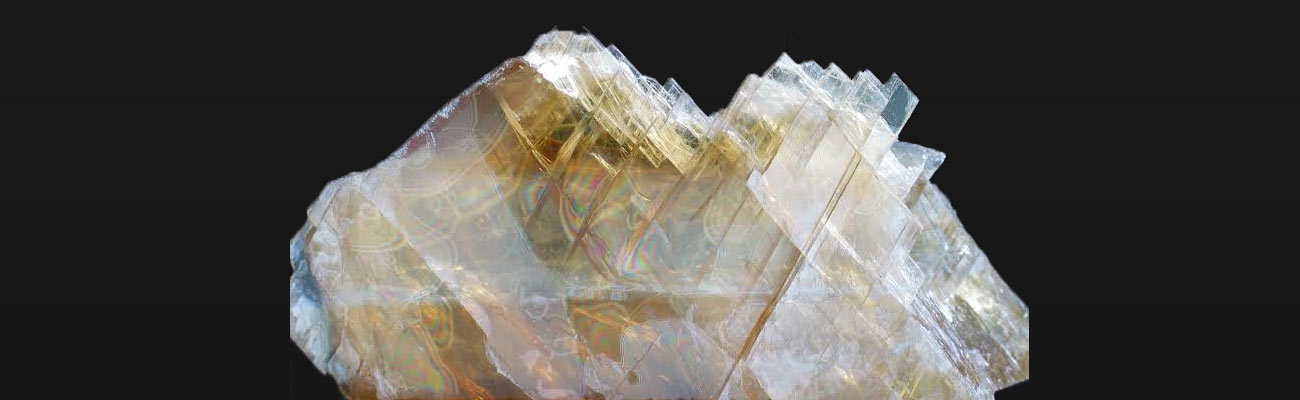
Calcium fluoride is a mineral composed of calcium fluoride (CaF2), the principal fluorine-bearing mineral. It occurs as cubic, isometric crystals and cleavable masses. When pure, it is colorless and transparent, or translucent with a glassy luster. Impurities cause color in the stone, and several varieties exhibit fluorescence. Usually found either in pure veins or associated with lead, silver, or zinc ores, it is common in limestone and dolomites.
Fluorite comes in a wide range of colors and has subsequently been dubbed “the most colorful mineral in the world”. The most common colors are purple, blue, green, yellow, or colorless. Less common are pink, red, white, brown, black, and nearly every shade in between. Color zoning or banding is commonly present. The color of the fluorite is determined by factors including impurities, exposure to radiation, and the size of the color centers.

Chemical Name: Fluorspar
Chemical Formula: CaF2
Chemical Properties
- Crude ore- 25 to 30%
- Metallurgical grade- 75 to 82%
- Ceramic grade- 94 to 96%
- Acid grade- 97%
- Crystalline grade- 99%
Typical Applications
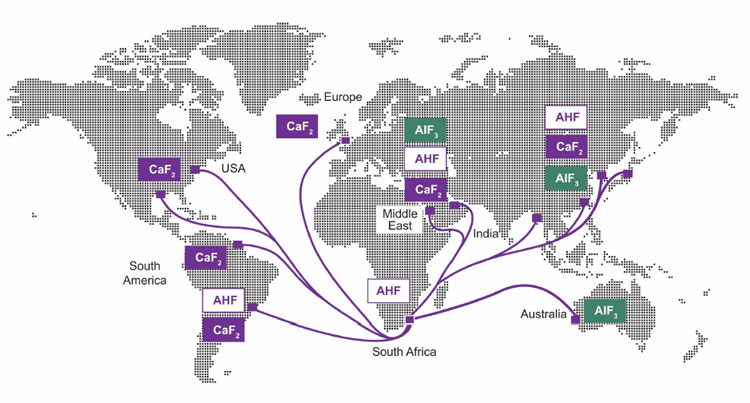
Calcium fluoride is a vital component in several industrial applications, including steel production. It is also used to make hydrogen fluoride (AHF) which, in turn, is used in the production of refrigerants and to make aluminum tri-fluoride (AlF3), critical in aluminum smelting; uranium fluoride (UF6), used in nuclear power stations; and lithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF6), used to make the electrolyte for lithium batteries.
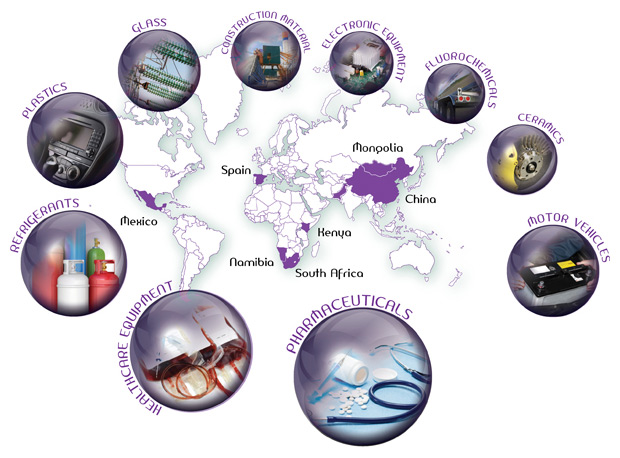
Other applications further downstream are:
- Refrigerants
- Ceramics
- Glass
- Plastics
- Healthcare Equipment
- Construction Materials
- Electronic And Electrical Equipment
- Motor Vehicles
- Pharmaceuticals
- Fluoro chemicals